PFA masterbatch is a plastic masterbatch mainly composed of perfluoroalkoxy polymer (PFA). PFA masterbatch is a type of plastic masterbatch with excellent properties, including super strong temperature resistance, chemical resistance, electrical performance, etc. It can maintain stable performance in harsh environments. Its highly fluorinated structure endows it with extremely high chemical stability and corrosion resistance, and has broad application prospects in semiconductor manufacturing, chemical industry, electronic appliances, medical and other fields. With the continuous advancement of technology and the increasing demand for high-performance materials, the use of PFA masterbatch will become more extensive.
Classification
The classification of PFA masterbatch is mainly based on factors such as its composition, function, and application fields. The following are some common classification methods:
Classified by ingredients:
Pure PFA masterbatch: mainly composed of perfluoroalkoxy polymer (PFA), without adding other additives or fillers, retaining the excellent properties of PFA itself.
Modified PFA masterbatch: On the basis of pure PFA resin, flame retardants, antibacterial agents, toughening agents, fillers and other additives are added to improve the specific properties of the masterbatch, such as flame retardancy, antibacterial properties, mechanical strength, etc.
Classified by function:
Flame retardant PFA masterbatch: Added flame retardant to improve the flame retardant performance of the masterbatch, suitable for fields with high requirements for fire safety.
Antibacterial PFA masterbatch: Added with antibacterial agents, it has the function of inhibiting bacterial growth and is suitable for fields with high hygiene requirements such as medical and food packaging.
Toughened PFA masterbatch: By adding toughening agents, the flexibility and impact resistance of the masterbatch are improved, making it suitable for products that need to withstand certain impact forces.
Filling PFA masterbatch: Fillers such as glass fiber, carbon fiber, etc. are added to improve the mechanical strength and heat resistance of the masterbatch, while reducing costs.
Classified by application field:
Semiconductor grade PFA masterbatch: used for manufacturing high-purity chemical containers, pipelines, etc. in the semiconductor manufacturing process, with extremely high requirements for purity and cleanliness.
Chemical grade PFA masterbatch: used for manufacturing chemical equipment, pipelines, valves, etc., requiring excellent chemical corrosion resistance.
Electronic and electrical grade PFA masterbatch: used for manufacturing insulation layers for wires and cables, packaging materials for electronic components, etc., requiring good electrical performance and temperature resistance.
Medical grade PFA masterbatch: used for manufacturing medical devices, biomedical polymer materials, etc., requiring good biocompatibility and degradability (under certain specific conditions).
These classification methods are not isolated, in fact, a PFA masterbatch may belong to multiple categories simultaneously. For example, a PFA masterbatch with added flame retardant and toughening agent belongs to both flame retardant PFA masterbatch and toughening PFA masterbatch, and may also belong to electronic or medical grade PFA masterbatch, depending on its final application field and performance requirements.
Fórmula
The proportion of different PFA masterbatch formulations is mainly adjusted according to the required performance and application fields. Here are some common PFA masterbatch formula ratios and their characteristics:
1. Pure PFA masterbatch
Formula ratio: mainly composed of perfluoroalkoxy polymer (PFA), usually accounting for more than 90%, with the rest being a small amount of processing aids.
Features: It retains the excellent properties of PFA itself, such as chemical resistance, heat resistance, electrical insulation, etc.
2. Flame retardant PFA masterbatch
Formula ratio: PFA resin accounts for about 70%~85%, flame retardants (such as decabromodiphenyl ether, antimony trioxide, etc.) account for about 10%~25%, and the rest are processing aids.
Features: Improved flame retardant performance of masterbatch, suitable for fields with high requirements for fire safety.
3. Antibacterial PFA masterbatch
Formula ratio: PFA resin accounts for about 80%~90%, antibacterial agents (such as silver ions, nano zinc oxide, etc.) account for about 5%~15%, and the rest are processing aids.
Characteristics: It has the function of inhibiting bacterial growth and is suitable for fields with high hygiene requirements such as medical and food packaging.
4. Toughened PFA masterbatch
Formula ratio: PFA resin accounts for about 60%~80%, toughening agents (such as elastomers, plasticizers, etc.) account for about 15%~35%, and the rest are processing aids.
Features: Improved the flexibility and impact resistance of the masterbatch, suitable for products that need to withstand certain impact forces.
5. Fill PFA masterbatch
Formula ratio: PFA resin accounts for about 50%~70%, fillers (such as glass fiber, carbon fiber, talcum powder, etc.) account for about 25%~45%, and the rest are processing aids.
Features: Improved the mechanical strength and heat resistance of the masterbatch, while reducing costs.
precautions
The formula ratio needs to be precise: different application fields have different performance requirements for PFA masterbatch, so the formula ratio also needs to be precisely controlled.
Careful selection of additives: The type and amount of additives have a significant impact on the performance of the masterbatch, and should be carefully selected according to specific needs.
Processing technology needs to be optimized: Different formula ratios may require different processing parameters, such as temperature, pressure, screw speed, etc., which need to be optimized to ensure the quality and performance of the masterbatch.
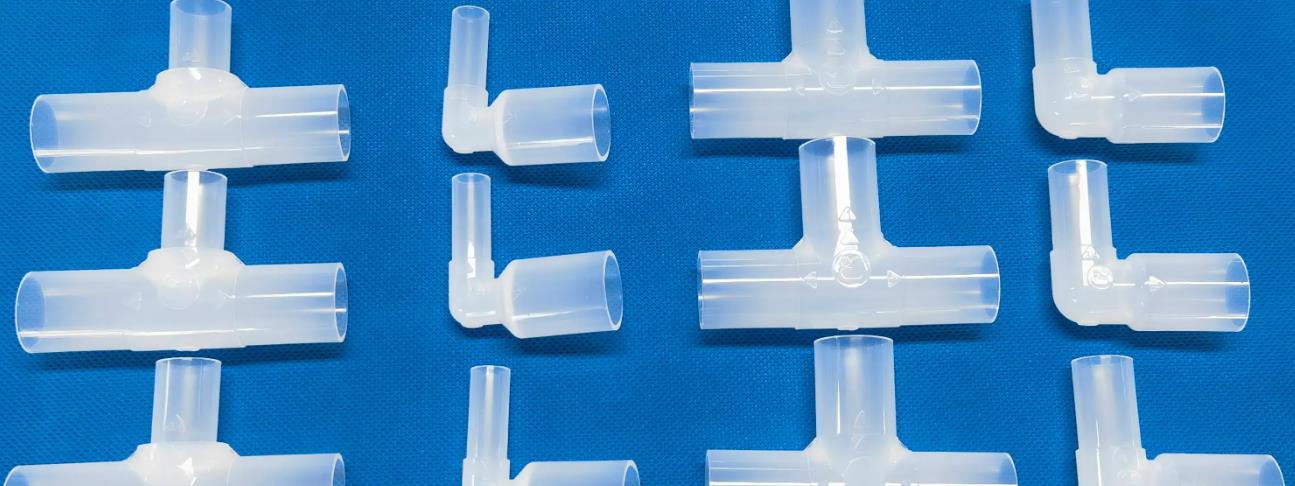
Proceso de producción
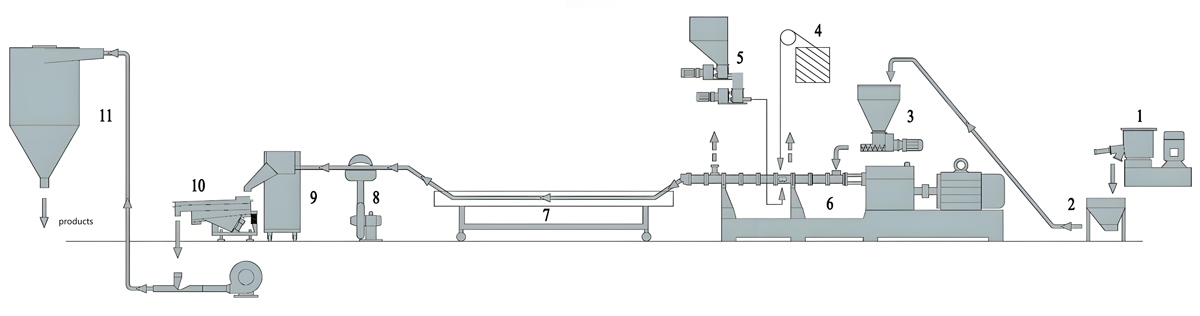
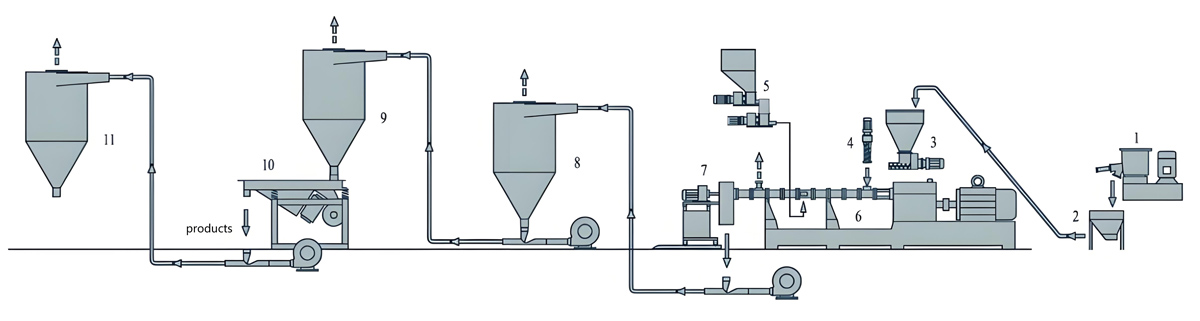
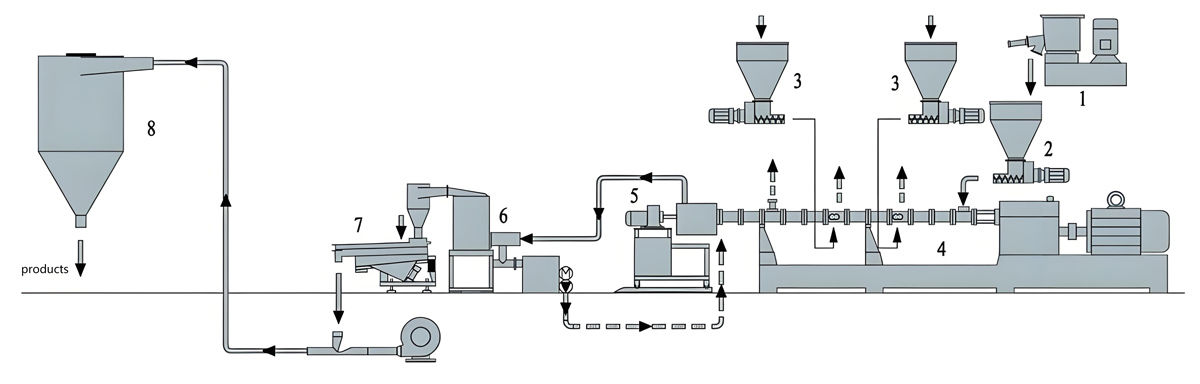
The production process of PFA masterbatch mainly includes steps such as raw material preparation, mixing, extrusion, cutting, drying, and packaging, among which extrusion molding is the key link.
Raw material preparation:
Accurately weigh perfluoroalkoxy polymer (PFA) resin, additives (such as flame retardants, antibacterial agents, toughening agents, fillers, etc.) and processing aids according to the required PFA masterbatch formula ratio.
Ensure that the purity and quality of raw materials meet production requirements.
Mixing:
Mix the weighed raw materials thoroughly in a high-speed mixer to ensure even distribution of each component.
The mixing time and speed need to be adjusted according to the characteristics of the raw materials and the requirements of the formula.
Extrusion molding:
Use a twin-screw extruder for extrusion molding. The extruder should be equipped with a precise temperature control system that can accurately control the temperature of the barrel and head, typically between 350-400 ℃.
The design of the screw should take into account the high viscosity and low flowability of PFA to ensure that the material can be fully plasticized and uniformly mixed during the extrusion process.
During the extrusion process, it is necessary to strictly control parameters such as screw speed and pressure to ensure the quality and performance of the masterbatch.
Granulation:
The extruded melt is cut into uniform granular masterbatch through a cutting system.
The cutting speed and the design of the cutting blade need to be adjusted according to the particle size requirements of the mother particle.
Drying and packaging:
The mother granules after cutting need to be dried to remove moisture and residual solvents.
The dried masterbatch is packaged for storage and transportation. The packaging material should have good sealing and moisture resistance.
The production process may be adjusted for different types of PFA masterbatch:
Flame retardant PFA masterbatch: It is necessary to accurately weigh the flame retardant during the mixing stage and strictly control the temperature during the extrusion process to avoid the decomposition or failure of the flame retardant.
Antibacterial PFA masterbatch: The antibacterial agent needs to be dispersed at the nanoscale in PFA resin, and special dispersion techniques need to be used during the mixing stage. Environmental hygiene must be strictly controlled during the production process.
Toughened PFA masterbatch: The addition of toughening agents may affect the processing performance of PFA, and extrusion parameters need to be adjusted to ensure the quality and performance of the masterbatch.
Filling PFA masterbatch: The amount of filler added is relatively large, and it is necessary to ensure the uniform dispersion of the filler in PFA resin. During the extrusion process, the screw speed and pressure should be controlled to avoid filler aggregation or blockage of the screw.
Production equipment
The production equipment for PFA masterbatch mainly includes extruders, mixers, pelletizers, dryers, and packaging machines.
Extruder:
Type: PFA masterbatch is usually produced using twin-screw extruders due to their excellent mixing and plasticizing capabilities.
Screw design: The screw should be designed according to the characteristics of PFA, such as aspect ratio, pitch, etc., to ensure that the material can be fully plasticized and evenly mixed during the extrusion process.
Temperature control: The extruder should be equipped with a precise temperature control system that can accurately control the temperature of the barrel and head to adapt to the high melting point characteristics of PFA.
Blender:
Function: Used to thoroughly mix PFA resin, additives, fillers and other raw materials to ensure uniform distribution of each component.
Type: Commonly used mixers include high-speed mixers, low-speed mixers, etc. The selection should be based on the characteristics of the raw materials and production needs.
Granulator:
Function: Cut the extruded melt into uniform granular masterbatch.
Type: There are various types of pelletizers, such as hot cutting pelletizers, cold pelletizers, etc. The selection should be based on the particle size requirements and production efficiency of the mother granules.
Drying machine:
Function: Dry the cut masterbatch to remove moisture and residual solvents, ensuring the quality of the masterbatch.
Type: Commonly used dryers include hot air circulation dryer, vacuum dryer, etc.
Packer:
Function: Packaging the dried masterbatch for storage and transportation.
Type: There are various types of packaging machines, such as automatic packaging machines, semi-automatic packaging machines, etc. The selection should be based on the production scale and packaging requirements.
The production equipment for PFA masterbatch needs to be selected based on multiple factors such as raw material characteristics, production requirements, and product quality. As the core equipment, the design and temperature control of the extruder are particularly critical. At the same time, auxiliary equipment such as mixers, pelletizers, dryers, and packaging machines also need to be reasonably configured according to the production process to ensure efficient and stable production of PFA masterbatch.
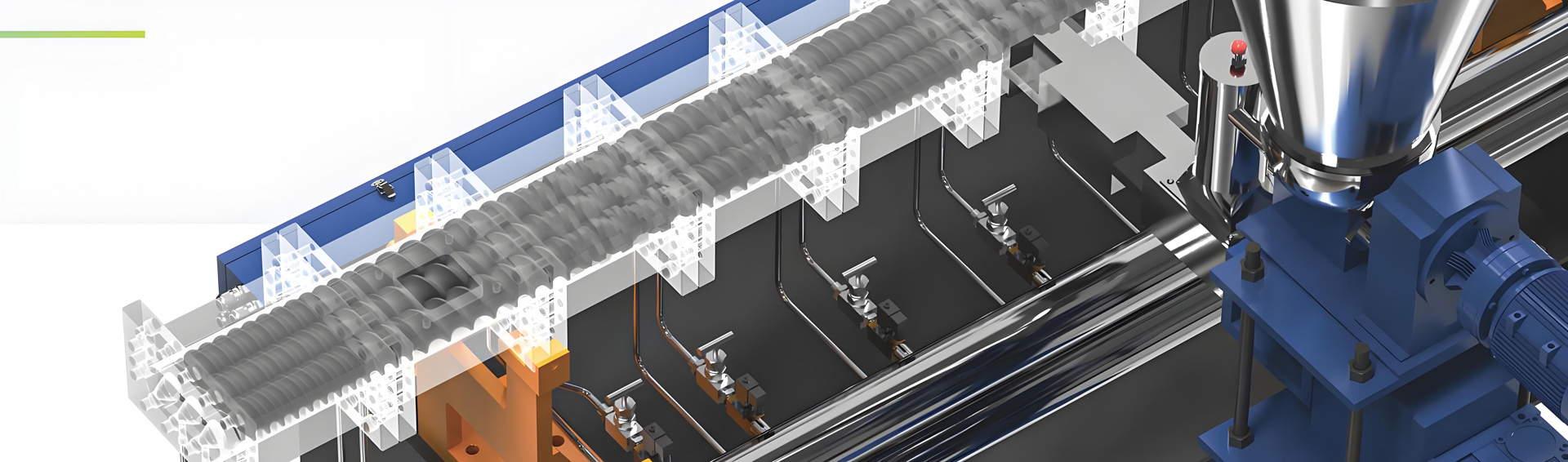
PFA masterbatch extruder
Kerke’s masterbatch extruder can be used to produce PFA masterbatch. Our PFA masterbatch extruder has multiple models to choose from, which can meet different production requirements.
-

Extrusora de doble husillo para laboratorio
¿Cuándo necesitará una extrusora de doble husillo de laboratorio? Si desea realizar ensayos y pruebas de...
-
Extrusora de doble husillo paralelo
Nuestra extrusora de doble husillo paralelo corrotante está diseñada para la fabricación de compuestos y...
-
Extrusor triple (3 tornillos)
La extrusora de 3 tornillos es una nueva tecnología que tiene muchas ventajas. La extrusora de triple tornillo se utiliza principalmente...
-
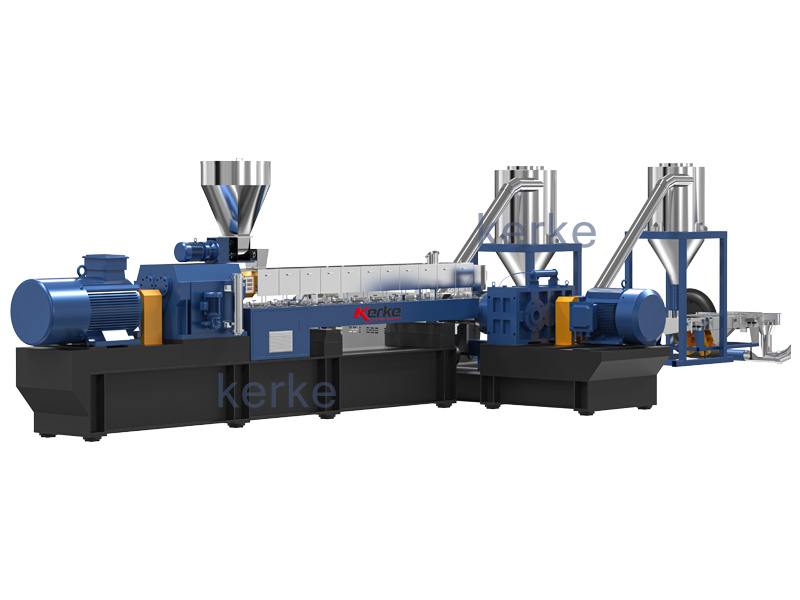

Sistema de extrusión de doble etapa
El sistema de extrusión madre-bebé está diseñado para materiales especiales que no pueden procesarse en una extrusora de una etapa,...
-
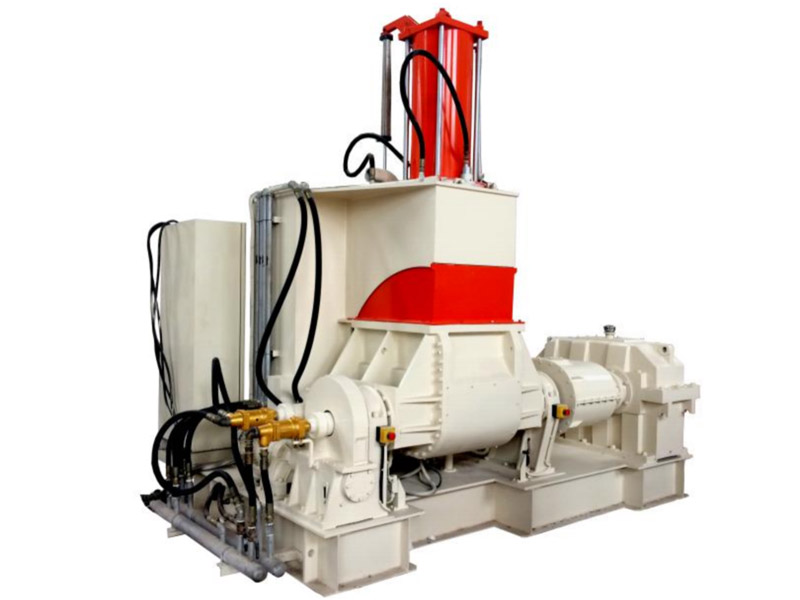

Línea de amasado Banbury
Nuestra amasadora + extrusora está diseñada para realizar aplicaciones especiales con una capacidad de producción de 30kg/h a 1000kg/h....
-
Sistema de corte / Sistema de granulación
Diferentes materiales necesitan diferentes sistemas de corte, Kerke ofrece todo tipo de sistemas de corte, aquí está la explicación de...
Related requirements
For the extruder used to produce PFA masterbatch, there are specific requirements as follows:
Temperature control capability:
The extruder should be equipped with a high-precision temperature control system that can accurately control the temperature of the barrel and head. The extrusion temperature of PFA is usually controlled between 330~425 ℃, so the extruder needs to be able to operate stably within this temperature range.
The material barrel should be divided into multiple heating sections for segmented heating according to the plasticizing requirements of the material, ensuring uniform and stable temperature during the extrusion process.
Screw design and material:
The screw should be designed based on the principle of building blocks, in order to reasonably configure the aspect ratio, pitch, screw components, etc. according to the processing material system and process requirements. For PFA, the aspect ratio of the screw is usually 20:1 to ensure sufficient plasticization and extrusion of the material.
The material of the screw should be corrosion-resistant and wear-resistant, such as 316 stainless steel, tungsten carbide, or ceramic screws, to cope with the high viscosity and low fluidity of PFA.
The screw structure should be optimized to improve plasticizing effect and exhaust performance, reduce the residence time of materials inside the screw, and avoid thermal degradation.
Motor power and gearbox transmission mode:
The motor power should be large enough to cope with the extrusion resistance caused by the high viscosity of PFA.
The transmission mode of the gearbox should be stable and reliable to ensure that the extruder operates smoothly at high speeds, reducing noise and vibration.
Extrusion volume and screw speed:
The extruder should be able to adjust the extrusion volume and screw speed according to production needs. The screw speed is usually set between 3-50r/min to balance production capacity and plasticizing effect.
The extrusion amount should be stable and controllable to ensure the uniformity of particle size and production efficiency of the masterbatch.
Exhaust system:
The extruder should be equipped with an effective exhaust system to eliminate the gas generated during the plasticization process of PFA, avoid the generation of bubbles, and ensure the quality of the masterbatch.
The exhaust port should be located above the material conveying direction and of moderate size to prevent materials from entering the exhaust system.
Equipment stability and reliability:
The extruder should have good stability to ensure the continuity and stability of the production process, reduce failures and downtime.
The equipment should be made of high-quality materials to ensure reliability and durability. At the same time, regular maintenance and upkeep of the equipment should be carried out to extend its service life.
Aplicación
The application of the extruder for producing PFA masterbatch is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
Semiconductor manufacturing: Ultra pure chemicals and materials are required in the semiconductor manufacturing process. Pipes, containers, and other components made of PFA masterbatch are widely used for transporting high-purity chemicals such as etchants and cleaning solutions due to their excellent chemical stability and low precipitation characteristics. The extruder needs to ensure the purity and quality of PFA masterbatch in this application to meet the high material requirements of semiconductor manufacturing.
Chemical industry: The chemical industry is facing challenges from various corrosive media such as strong acids, strong bases, and organic solvents. Pipes, valves, pumps and other components made of PFA masterbatch can resist the erosion of these corrosive media, ensuring the long-term stable operation of chemical equipment. When producing these components, extruders need to have good corrosion resistance and stability to adapt to the harsh environment of the chemical industry.
In the field of electronics and electrical engineering, PFA masterbatch is widely used in the manufacturing of insulation layers for wires and cables, as well as packaging materials for electronic components, due to its excellent electrical insulation performance and high temperature resistance. The extruder in this application requires precise control of the extrusion amount and size of PFA masterbatch to ensure the performance and reliability of electronic and electrical products.
Medical field: PFA masterbatch is used in the manufacturing of medical devices, biomedical polymer materials, etc. due to its good biocompatibility and degradability (under certain specific conditions). When producing these medical supplies, extruders need to ensure the purity and sterility of PFA masterbatch to meet the high material requirements in the medical field.
In addition, when producing PFA masterbatch, the extruder needs to be adjusted and optimized according to specific formula ratios and process requirements to ensure that the quality and performance of the masterbatch meet the needs of different application fields. For example, for flame retardant PFA masterbatch, the extruder needs to precisely control the amount of flame retardant added and the uniformity of dispersion; For antibacterial PFA masterbatch, the extruder needs to ensure the effectiveness and stability of the antibacterial agent.