Starch masterbatch is a granular material made mainly from plant starch (such as cassava, corn, potato starch), which is physically or chemically modified and compounded with carrier resins (such as PBAT, PLA) and additives. It is a functional masterbatch modified through special processes and widely used in environmental materials, packaging, agriculture, and other fields.
Characteristic
Biodegradability
100% bio based raw materials can be completely degraded into water and carbon dioxide under composting conditions, meeting degradation standards such as EU EN13432 and US ASTM D6400.
The degradation cycle is short, and it can be completely decomposed within 6-12 months under industrial composting conditions.
Processability
Through thermoplastic modification, starch masterbatch has good thermoplasticity and flowability, and can be directly blended with polymers such as PBAT and PE for blown film and injection molding.
Low melt index (≤ 5g/10min), wide processing temperature range (130-165 ℃), suitable for traditional plastic processing equipment.
Physical property
Film forming property: The produced film has good transparency and smooth surface, and can be blown into 1 filament (0.01mm) ultra-thin film.
Mechanical properties: Tensile strength ≥ 10MPa, elongation at break ≥ 300%, meeting daily packaging requirements.
Environmental advantages
Replace traditional plastics by 30% -50% and reduce carbon emissions.
Biomass content ≥ 99%, in line with the trend of green and sustainable development.
Types
Starch masterbatch can be classified according to different classification criteria, and the following are some common types:
Classification based on starch sources
Corn starch masterbatch: made mainly from corn starch. Corn starch has a high yield and low cost, and is a commonly used starch source for producing starch masterbatch. This masterbatch has good flowability and processability, and is widely used in fields such as plastic modification.
Potato starch masterbatch: made from potato starch. Potato starch granules are large and have a low gelatinization temperature. The mother granules made from them are widely used in products that require lower processing temperatures and have good flexibility.
Cassava starch masterbatch: based on cassava starch. Cassava starch has high purity and low protein content, and the masterbatch made from it performs well in terms of degradation performance. It is commonly used in biodegradable plastic products.
Classify based on added ingredients
Ordinary starch masterbatch: mainly composed of starch and a small amount of additives such as plasticizers, lubricants, etc., used for general plastic filling and modification, which can reduce the cost of plastic products and improve their processing performance to a certain extent.
Functional starch masterbatch:
Antibacterial starch masterbatch: added with antibacterial agents such as silver ions, nano zinc oxide, etc., to give the product antibacterial properties. It can be used in food packaging, medical supplies, and other fields, effectively inhibiting bacterial growth and extending product shelf life.
Flame retardant starch masterbatch: flame retardants such as magnesium hydroxide and phosphate esters are added to improve the flame retardant performance of plastic products, making them comply with relevant safety standards. It is commonly used in products with high flame retardant requirements such as electronic and electrical casings and building materials.
Water resistant starch masterbatch: By adding water-resistant agents such as silane coupling agents, the water resistance of starch masterbatch can be improved, allowing it to maintain good performance in humid environments or in contact with water. It can be used in some plastic products that require a certain degree of water resistance, such as outdoor products, aquaculture products, etc.
مصنفة حسب الغرض
Starch masterbatch for packaging: used in the production of various packaging materials, such as plastic bags, packaging films, disposable tableware, etc. These types of masterbatch typically require good film-forming properties, flexibility, and a certain level of strength to protect packaged items and meet the packaging industry’s requirements for environmental protection and degradability.
Agricultural starch masterbatch: mainly used for manufacturing agricultural products such as agricultural films and seedling bowls. The masterbatch is required to have good weather resistance, thermal insulation, and breathability to promote crop growth, while also being able to degrade quickly in the soil after use, reducing environmental pollution.
Starch masterbatch for injection molding: suitable for injection molding process, used in the production of various plastic parts, such as toys, stationery, daily necessities, etc. The masterbatch needs to have good fluidity and formability to ensure the quality and accuracy of injection molded products.
نسبة الصيغة
The formula ratio of different types of starch masterbatch may vary depending on the starch source, added ingredients, and uses. The following are approximate formula ratios for some common types of starch masterbatch:
Ordinary corn starch masterbatch
Corn starch: 60% -80%, as the main component, provides biodegradability and some physical properties.
Carrier resin: 15% -30%, commonly used include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), etc., to improve the processing and mechanical properties of masterbatch.
Plasticizers: 3% -10%, such as glycerol, citrate, etc., increase the flexibility and plasticity of starch, and reduce processing temperature.
Lubricant: 0.5% -2%, such as stearic acid, stearic acid salts, etc., to reduce friction between particles, improve flowability, and prevent mold sticking.
Antibacterial potato starch masterbatch
Potato starch: 50% -70%, using its characteristics as a basic raw material.
Carrier resin: 20% -30%, choose the appropriate resin according to specific needs.
Antibacterial agents: 0.5% -5%, such as silver ion antibacterial agents, nano zinc oxide, etc., provide antibacterial function.
Plasticizer: 5% -10%, improves the processing performance of starch and the flexibility of products.
Lubricant: 0.5% -2%, with the same function as the lubricant in ordinary masterbatch.
Water resistant cassava starch masterbatch
Cassava starch: 55% -75%, is the main component of the masterbatch.
Carrier resin: 15% -30%, plays a role in bearing and improving performance.
Waterproof agent: 3% -10%, such as silane coupling agent, to improve the water resistance of the masterbatch.
Plasticizer: 3% -8%, giving starch good processing properties.
Lubricant: 0.5% -2% to ensure smooth processing.
Starch masterbatch for flame retardant injection molding
Starch (can be mixed with various types of starch): 40% -60%, providing a certain degree of degradability and basic properties.
Carrier resin: 20% -30%, choose the appropriate resin according to the requirements of the injection molded product.
Flame retardant: 15% -30%, such as magnesium hydroxide, phosphate esters, etc., to achieve the required flame retardant level.
Plasticizer: 3% -8%, improves the processing performance of starch and resin.
Lubricant: 0.5% -2%, helps with material flow and demolding during the injection molding process.
The above formula ratios are for reference only. In actual production, adjustments and optimizations need to be made based on specific production equipment, process conditions, and product performance requirements.

عملية الإنتاج
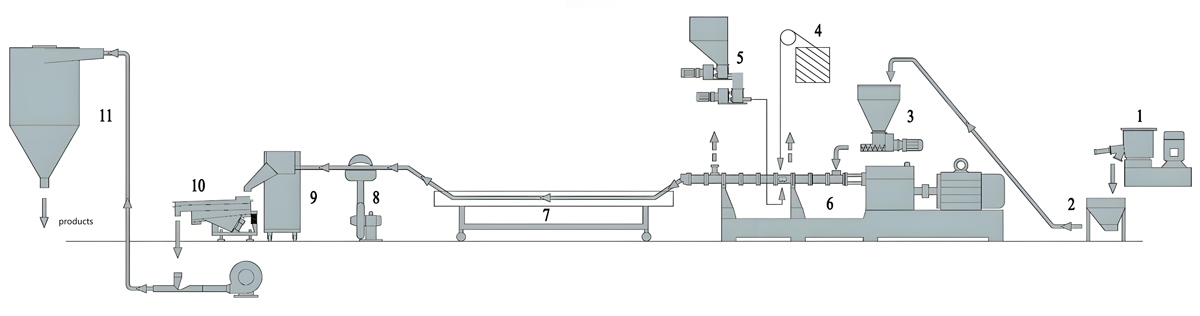
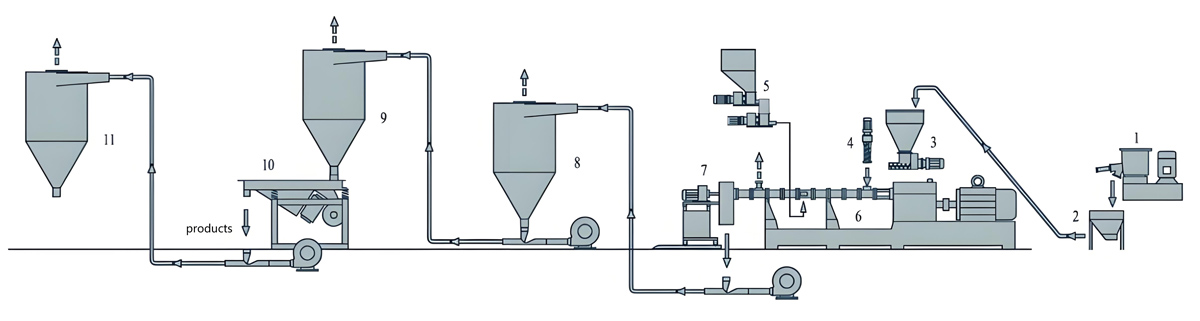
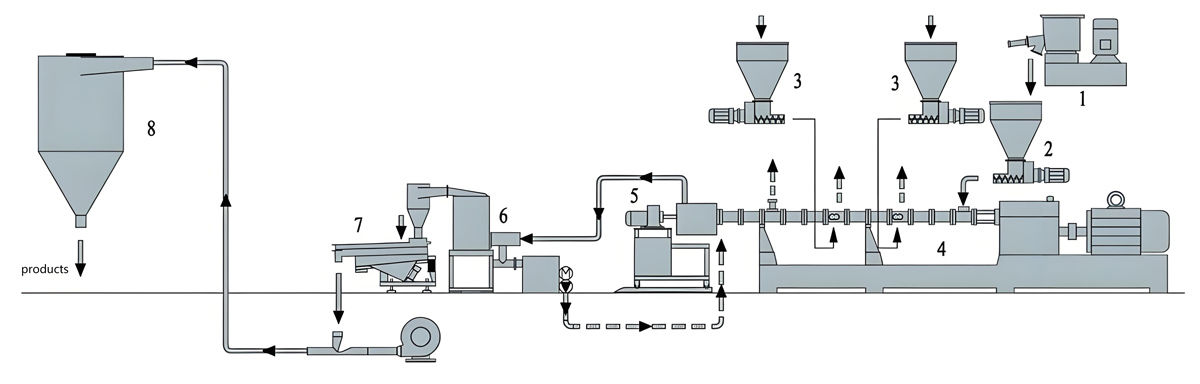
The production process of starch masterbatch usually includes steps such as raw material preparation, mixing, plasticization extrusion, cooling granulation, etc. The following is a specific introduction:
1. تحضير المواد الخام
Starch processing: Select the appropriate starch based on the type of starch masterbatch, such as corn starch, potato starch, or cassava starch. Drying the starch to reduce its moisture content to a certain extent, generally requiring a moisture content of less than 10%, to avoid problems such as bubbles and degradation caused by excessive moisture during processing.
Additive preparation: Accurately weigh various additives according to the formula, such as carrier resin, plasticizer, lubricant, antibacterial agent, flame retardant, etc. Ensure that the quality and purity of additives meet production requirements.
2. الخلط
Pre mixing: Pre mix the dried starch with additives in a high-speed mixer to achieve initial uniform dispersion of each component. The pre mixing time is generally 10-15 minutes, and the stirring speed is adjusted according to the characteristics of the raw materials and equipment performance, usually around 500-1000 revolutions per minute.
Mixing: The pre mixed material is then further mixed and plasticized in the mixing machine. The temperature, speed, and time of the mixer are key parameters. Generally, the temperature is controlled between 120-180 ℃, the speed is 30-60 revolutions per minute, and the mixing time is 10-20 minutes. Through mixing, starch and additives are thoroughly mixed evenly to form a uniform material with certain plasticity and fluidity.
3. Plasticized extrusion
Put the mixed material into a twin-screw extruder for plasticization and extrusion. Twin screw extruders have good mixing and conveying capabilities, which can further plasticize and uniformly mix materials under high temperature and high pressure.
The temperature setting of an extruder is usually divided into multiple sections, gradually increasing from the feed section to the machine head. The temperature of the feed section is generally 100-120 ℃, the temperature of the middle section is 140-160 ℃, and the temperature of the machine head is 160-180 ℃. The screw speed is adjusted according to the characteristics of the material and the production requirements, generally between 100-300 revolutions per minute.
During the extrusion process, the material moves forward under the push of the screw, while being subjected to shear and friction forces, causing it to fully plasticize and mix. Squeeze continuous strip or sheet materials through the die mouth of the machine head.
4. Cooling granulation
Air cooling or water cooling: The extruded material is cooled and shaped by air cooling or water cooling. Air cooling is the use of air convection to remove heat and rapidly cool materials; Water cooling is the process of cooling materials through a water tank, with a fast cooling rate. However, it is important to control the temperature of the cooling water to avoid internal stress or surface defects caused by sudden cooling of the materials.
Granulation: The cooled material is granulated by a granulator and cut into particles of a certain size. The tool speed and cutting length of the granulator are adjusted according to the required particle size. The common particle size is generally between 2-5 millimeters.
5. Screening and packaging
Screening: The starch masterbatch after granulation is screened through a vibrating screen to remove particles that are too large or too small, ensuring the uniformity of the product’s particle size. The mesh size of the sieve is selected according to product requirements, and the commonly used mesh size is between 20-60 mesh.
Packaging: The qualified starch masterbatch after screening is sealed to prevent moisture absorption and contamination. Packaging materials usually use plastic bags or composite packaging bags with good moisture resistance, and indicate the product name, specifications, production date, shelf life, and other information on the packaging.
In the production process, it is necessary to optimize and adjust the process parameters according to the characteristics and requirements of different types of starch masterbatch to ensure the quality and stable performance of the product. At the same time, regular maintenance and upkeep of production equipment are necessary to ensure its normal operation and achieve efficient and stable production.
معدات الإنتاج
The equipment for producing starch masterbatch mainly includes raw material processing equipment, mixing equipment, extrusion equipment, cooling equipment, granulation equipment, and screening and packaging equipment. The following is a specific introduction:
1. معدات معالجة المواد الخام
Drying machine: used for drying starch raw materials to reduce their moisture content. Common drying machines include airflow drying machines, fluidized bed drying machines, etc. The airflow dryer suspends and dries starch particles through high-speed hot air flow, with a fast drying speed; The fluidized bed dryer dries starch in a fluidized state formed by hot air, resulting in uniform drying effect.
2. المعدات الهجينة
High speed mixer: used for preliminary mixing of starch with various additives. It has high-speed rotating stirring blades that can achieve a certain degree of uniform mixing of materials in a short period of time, laying the foundation for subsequent mixing and extrusion processes.
Internal mixer: further mixing and plasticizing of materials that have been preliminarily mixed. The rotor of the internal mixer has a special shape, which can generate strong shear and mixing effects, allowing starch and additives to be fully mixed evenly under high temperature and high pressure, forming materials with good plasticity and uniformity.
3. معدات البثق
Twin screw extruder: It is one of the key equipment for starch masterbatch production. It has two interlocking screws that can efficiently transport, mix, plasticize, and extrude materials. By reasonably setting parameters such as temperature, speed, and screw combination of the extruder, the material can achieve ideal plasticization effect and uniformity during the extrusion process, ensuring product quality.
4. معدات التبريد
Air cooling system: composed of fans, air ducts, etc., it takes away the heat of extruded materials through forced air flow, allowing them to quickly cool and solidify. The air-cooled system has a simple structure and easy operation, suitable for situations where cooling speed is not particularly high, and can effectively avoid internal stress or surface defects caused by rapid cooling of materials.
Water cooling system: usually includes components such as water tank and circulating water pump. The extruded material is cooled through a water tank. Due to the high specific heat capacity of water, the cooling rate is faster than air cooling, which can improve production efficiency. But it is necessary to pay attention to controlling the cooling water temperature to ensure product quality.
5. معدات التحبيب
Granulator: installed after the extruder outlet or cooling equipment, used to cut the cooled strip or sheet materials into particles of a certain size. The cutting speed and cutting length of the granulator can be adjusted according to the required particle size to meet the particle size requirements of different products.
6. Screening and packaging equipment
Vibration screen: used to screen the starch masterbatch after granulation, remove particles that are too large or too small, and ensure the uniformity of product particle size. The vibrating screen generates vibration through a vibration motor, causing particles to bounce and sieve on the screen. Different mesh sizes of screens can be selected according to product requirements.
Packaging machine: used for packaging qualified starch masterbatch after screening. Common packaging machines include automatic measuring packaging machines, vacuum packaging machines, etc. The automatic measuring and packaging machine can accurately measure and package products of a certain weight, improving packaging efficiency and accuracy; Vacuum packaging machines are suitable for products that require high moisture and oxidation resistance, and can extend the shelf life of the products.
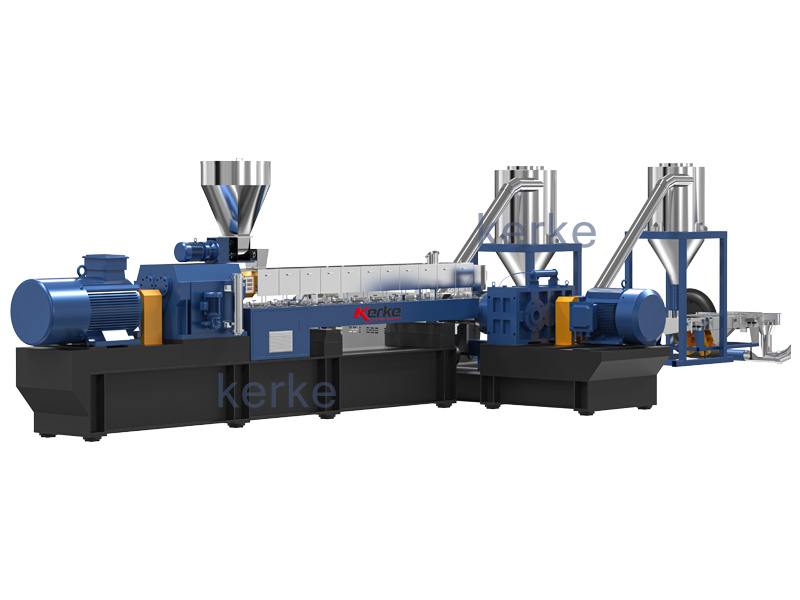
Starch masterbatch extruder
Kerke’s masterbatch extruder can be used to produce starch masterbatch. Our starch masterbatch extruder has multiple models to choose from, which can meet different production requirements.
-

آلة البثق اللولبية المزدوجة للمختبر
متى ستحتاج إلى آلة بثق ثنائية اللولب للمختبر؟ إذا كنت ترغب في إجراء تجارب واختبارات...
-
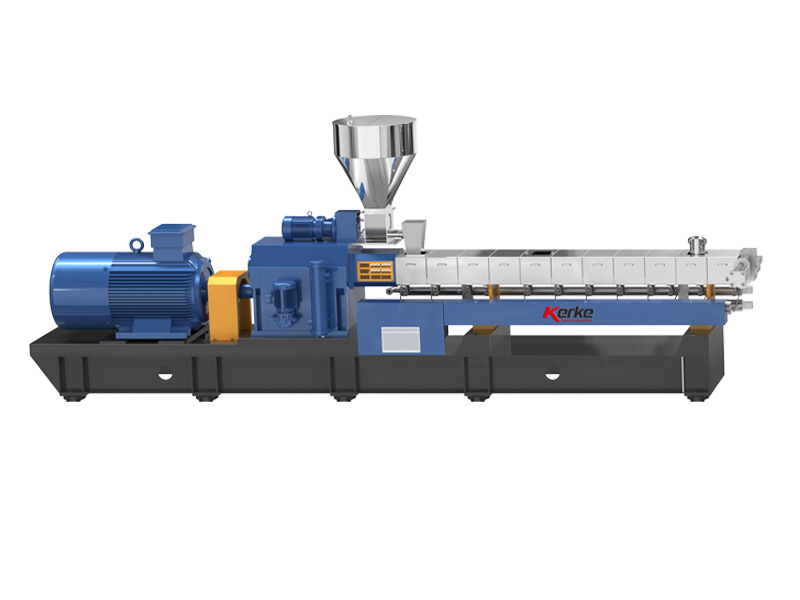
آلة البثق ذات اللولب المزدوج المتوازي
تم تصميم آلة البثق ذات المسمار المزدوج ذات الدوران المتوازي لدينا لتصنيع المركبات والدفعات الرئيسية مع سعة إنتاج تتراوح من...
-
طارد ثلاثي (3 براغي)
آلة البثق ثلاثية البراغي هي تقنية جديدة ذات مزايا عديدة. تُستخدم آلة البثق ثلاثية البراغي بشكل رئيسي...
-

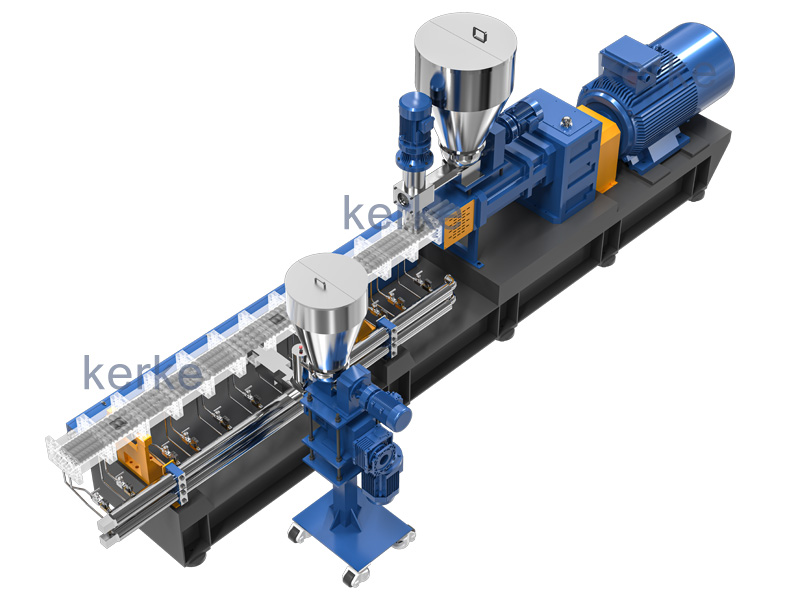
نظام البثق ثنائي المرحلة
تم تصميم نظام بثق الأم والطفل للمواد الخاصة التي لا يمكن معالجتها على مرحلة واحدة من البثق، المرحلة الأولى...
-

خط تصنيع العجنات في بانبوري
تم تصميم آلة العجن والبثق الخاصة بنا لصنع تطبيقات خاصة بسعة إنتاج تتراوح من 30 كجم / ساعة إلى 1000 كجم / ساعة.
-
نظام القطع / نظام التكوير
تحتاج المواد المختلفة إلى نظام قطع مختلف، توفر شركة Kerke جميع أنواع أنظمة القطع، فيما يلي شرح لها…
Related requirements
The extruder is a key equipment for producing starch masterbatch, and its parameter settings have a significant impact on product quality and production efficiency. The following are common parameter settings for extruders:
Temperature setting
Feeding section: generally set at 100-120 ℃. This area is mainly used to allow the material to soften initially when heated, while avoiding premature gelatinization of starch caused by high temperature, which may affect subsequent processing.
Middle section: The temperature is usually controlled between 140-160 ℃. In the middle section, the material begins to further plasticize, and starch and additives gradually mix evenly. Appropriate temperature helps to improve the flowability and plasticity of the material.
Head section: The head temperature is generally 160-180 ℃. A higher temperature can make the material have good flowability during extrusion, making it easier to extrude from the machine head, while ensuring a smooth surface of the product and reducing defects.
Screw speed setting
The screw speed is adjusted according to the material characteristics and production requirements, generally between 100-300 revolutions per minute. A lower rotational speed is beneficial for the thorough mixing and plasticization of materials, but the production efficiency is lower; A higher rotational speed can increase production, but it may cause material shear overheating and affect product quality. In actual production, it is necessary to find the balance point between rotational speed, product quality, and output based on specific circumstances. For example, for starch materials with high viscosity, the rotational speed should be appropriately reduced to avoid excessive shearing; For materials with good fluidity, the rotational speed can be appropriately increased to increase production.
Screw torque setting
The screw torque reflects the load borne by the screw during the extrusion process, which is related to factors such as material viscosity, filling amount, and screw speed. Appropriate screw torque setting can ensure the stability of the extrusion process and product quality. Generally speaking, the range of screw torque should be set according to the characteristics of the material and the performance of the equipment, usually between 30% and 70% of the rated torque of the equipment. If the torque is too high, it may cause problems such as increased screw wear and motor overload; If the torque is too low, it may indicate incomplete plasticization of the material or insufficient extrusion volume.
Pressure setting
Feed inlet pressure: The feed inlet pressure is generally kept at a low level to avoid excessive resistance to the material during feeding, which may affect the smoothness of feeding. Usually, the inlet pressure is set between 0.5-1.5 MPa.
Head pressure: Head pressure is crucial for ensuring the compactness of extruded materials and the dimensional accuracy of products. The general head pressure is set between 5-15MPa. By adjusting the throttle device or mold structure at the head, the head pressure can be controlled within an appropriate range. If the head pressure is too high, it may lead to increased mold wear and difficulty in material extrusion; If the pressure is too low, it may cause defects such as pores and uneven surfaces in the product.
When setting the parameters of the extruder, it is necessary to comprehensively consider factors such as the type of starch raw material, the formula of additives, the quality requirements of the product, and the performance of the equipment. Through multiple experiments and adjustments, the most suitable parameter combination should be found to achieve stable and efficient production.
طلب
Starch masterbatch has a wide range of applications in multiple fields, and the following are some of the main application aspects:
Plastic industry
Filling modification: Adding starch masterbatch to plastics can reduce the production cost of plastics. Meanwhile, the addition of starch can also improve the processing performance of plastics, such as increasing fluidity and reducing melt viscosity. For example, adding an appropriate amount of starch masterbatch to common plastics such as polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) can improve the hardness and rigidity of plastic products while maintaining good toughness.
Biodegradation: Starch is a naturally biodegradable polymer material, and adding starch masterbatch to plastics can give them a certain degree of biodegradability. Over time, starch will be decomposed by microorganisms in the natural environment, causing plastic products to gradually disintegrate and reducing environmental pollution. This biodegradable plastic has broad application prospects in fields such as packaging and agricultural films. For example, starch based biodegradable plastic bags can decompose quickly in soil after use, reducing white pollution.
Textile industry
Starch masterbatch can be used as a textile sizing agent after modification. It can form a uniform slurry film on the surface of the yarn, improve the strength, wear resistance, and smoothness of the yarn, reduce the breakage rate of the yarn during weaving, and improve weaving efficiency and fabric quality. Compared with traditional chemical sizing agents, starch based sizing agents have good biodegradability and environmental friendliness.
Fabric finishing agent: A finishing agent made from starch masterbatch applied to fabric finishing can improve the feel, softness, and drape of the fabric. At the same time, starch finishing agents can also endow fabrics with certain wrinkle resistance and moisture absorption, improving the comfort of wearing fabrics. For example, in the finishing of cotton fabrics, the use of starch finishing agents can make the fabric softer and smoother, while increasing its sweat absorption and breathability.
Paper industry
Paper enhancer: Starch masterbatch can be added as a paper enhancer to papermaking materials. It can interact with cellulose fibers in paper to form hydrogen bonds, thereby improving the strength properties of paper, such as tensile strength, burst resistance, and tear resistance. In the production of various types of paper such as cultural paper and packaging paper, adding an appropriate amount of starch masterbatch can effectively improve the quality and performance of the paper.
Surface sizing agent: Starch masterbatch is used for surface sizing of paper, which can form a uniform adhesive film on the surface of the paper, improving the surface strength, smoothness, and printability of the paper. This layer of adhesive film can effectively prevent paper from shedding hair and powder during the printing process, improving printing quality. Meanwhile, starch based surface sizing agents can also improve the water resistance of paper, enabling it to maintain good performance in humid environments.
مناطق أخرى
In the agricultural field, starch masterbatch can be used to prepare agricultural water retaining agents. The water retaining agent made by copolymerizing or blending starch with some hydrophilic polymer materials has good water absorption and retention properties. It can absorb and store a large amount of water in the soil, slowly release it for plant absorption and utilization, thereby improving the soil’s water retention performance, reducing irrigation water consumption, and promoting plant growth. In addition, starch masterbatch can also be used to prepare biodegradable agricultural films, providing environmentally friendly covering materials for agricultural production.
In the pharmaceutical field, starch masterbatch can be used to prepare drug sustained-release carriers. By encapsulating drugs in starch based materials, utilizing the biodegradability and controllable degradation rate of starch, slow drug release can be achieved, prolonging the drug’s action time and improving its efficacy. Meanwhile, starch masterbatch can also be used as a medicinal excipient for tablet molding, disintegration, and other purposes. For example, in some oral tablets, starch acts as a disintegrant, which can rapidly disintegrate the tablet in the gastrointestinal tract, releasing the drug components for easy absorption by the human body.