PBS masterbatch is a granular plastic masterbatch mainly composed of polybutylene succinate (PBS), processed by adding additives, fillers, and other equipment such as extruders. PBS is a completely biodegradable material that can be decomposed into carbon dioxide and water by microorganisms under natural conditions. It is environmentally friendly and has high tensile strength and good flexibility. Its mechanical strength is similar to that of general plastics such as polypropylene and polyethylene. PBS masterbatch can adapt to various preparation processes such as injection molding, extrusion, blown film, and lamination, and is easy to process and shape.
Classification
The classification of PBS masterbatch is mainly based on its different components, functions, and application fields. The specific classification is as follows:
Ingredient classification:
Pure PBS masterbatch: mainly made of polybutylene succinate (PBS) resin, without adding other additives or fillers.
Modified PBS masterbatch: On the basis of pure PBS resin, flame retardants, antibacterial agents, toughening agents, fillers and other additives are added to improve the specific properties of the masterbatch.
Functional classification:
Flame retardant PBS masterbatch: Added flame retardant to improve the flame retardant performance of the masterbatch, suitable for fields with high flame retardant requirements, such as electronic appliances, automotive interiors, etc.
Antibacterial PBS masterbatch: Added with antibacterial agents, it has the function of inhibiting bacterial growth and is suitable for fields with high hygiene requirements such as medical and food packaging.
Toughened PBS masterbatch: By adding toughening agents, the flexibility and impact resistance of the masterbatch are improved, making it suitable for products that need to withstand certain impact forces.
Filling PBS masterbatch: Adding fillers such as calcium carbonate, talc powder, etc. reduces the cost of masterbatch and may improve certain properties such as rigidity and heat resistance.
Application classification:
PBS masterbatch for packaging: mainly used in the production of biodegradable food packaging, garbage bags, cosmetic bottles and other packaging materials.
Agricultural PBS masterbatch: used for the production of agricultural films, slow-release fertilizers, and other agricultural products to promote sustainable agricultural development.
Medical PBS masterbatch: Due to its good biocompatibility and biological absorbability, medical PBS masterbatch is mainly used for the production of biomedical polymer materials such as artificial cartilage, sutures, and scaffolds.
Other specialized PBS masterbatch: customized PBS masterbatch produced according to specific application needs, such as disposable tableware, daily necessities, etc.
These classification methods are not isolated, in fact, a PBS masterbatch may belong to multiple classifications simultaneously. For example, a PBS masterbatch with added flame retardant and toughening agent belongs to both flame retardant and toughening PBS masterbatch, and may also belong to packaging or agricultural PBS masterbatch, depending on its final application field.
Formula ratio
The proportion of different types of PBS masterbatch formulations may vary depending on specific application requirements. Here are some common types of PBS masterbatch and their approximate formula ratios:
1. Pure PBS masterbatch
Formula ratio: mainly composed of polybutylene succinate (PBS), usually accounting for more than 95%, and the rest may contain small amounts of processing aids such as antioxidants, lubricants, etc. to improve processing performance.
2. Flame retardant PBS masterbatch
Formula ratio: On the basis of pure PBS, flame retardants such as decabromodiphenyl ether and antimony trioxide are added. The amount of flame retardant added is usually between 10% and 30%, depending on the required flame retardant grade and the basic performance of PBS.
3. Antibacterial PBS masterbatch
Formula ratio: Add antibacterial agents such as silver ions, nano zinc oxide, etc. to PBS. The amount of antibacterial agent added is generally low, usually between 1% and 5%, to ensure antibacterial effect without affecting other properties of PBS.
4. Toughened PBS masterbatch
Formula ratio: In order to improve the flexibility and impact resistance of PBS, toughening agents such as elastomers (such as SBS, SEBS), plasticizers, etc. can be added. The amount of toughening agent added is usually between 5% and 20%, depending on the desired toughening effect and the basic properties of PBS.
5. Fill PBS masterbatch
Formula ratio: In order to reduce costs or improve certain properties such as rigidity and heat resistance, fillers such as calcium carbonate, talc powder, glass fiber, etc. can be added to PBS. The amount of filler added can range from 10% to 50%, or even higher, depending on the application requirements and the basic performance of PBS.
6. Special function PBS masterbatch
Formula ratio: According to specific application requirements, other special functional additives such as anti-static agents, UV absorbers, light stabilizers, etc. can also be added. The amount of these additives added is usually low to ensure that it does not affect the basic properties of PBS.
Precautions
The formula ratio needs to be adjusted according to specific application requirements: the formula ratio of different types of PBS masterbatch may vary depending on their application fields. Therefore, in practical applications, it is necessary to adjust the formula ratio according to specific needs.
Ensure compatibility between components: When adding additives or fillers, it is necessary to ensure their compatibility with PBS resin to avoid negative effects on the performance of the masterbatch.
Considering processing performance: The adjustment of formula ratios also needs to take into account the impact of processing performance. For example, adding too much filler may affect the flowability of the masterbatch, thereby affecting processing efficiency.

Production process
Different types of PBS masterbatch may have differences in production processes, but overall, they all follow certain basic steps. The following is an overview of the production processes for different types of PBS masterbatch:
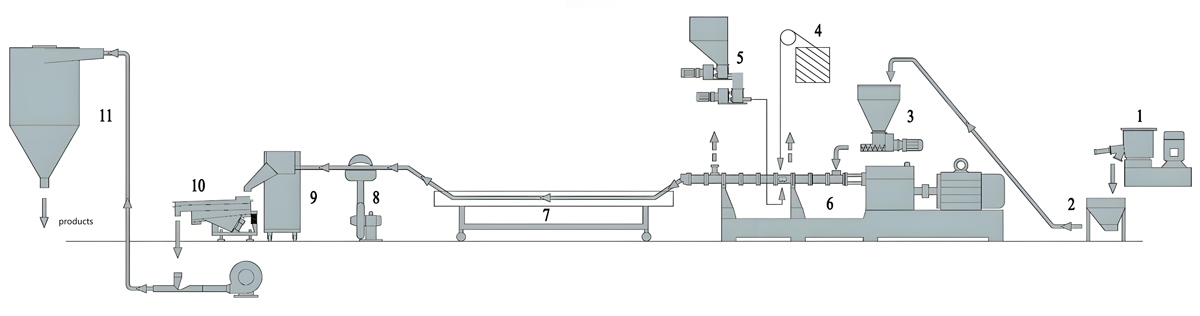
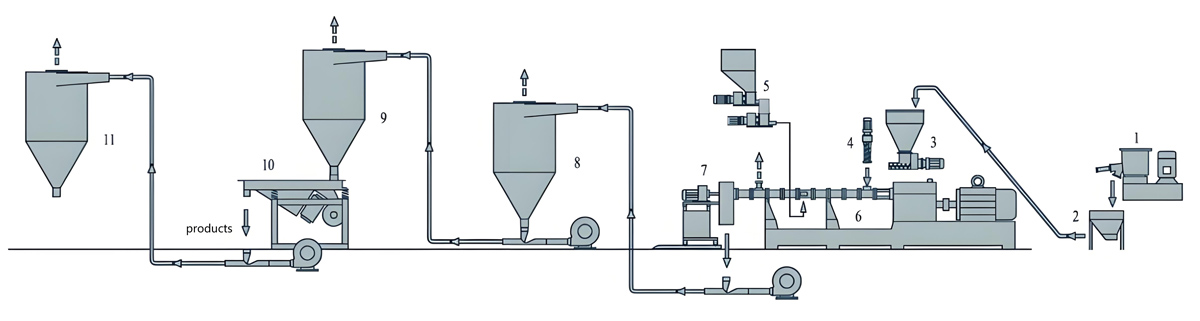
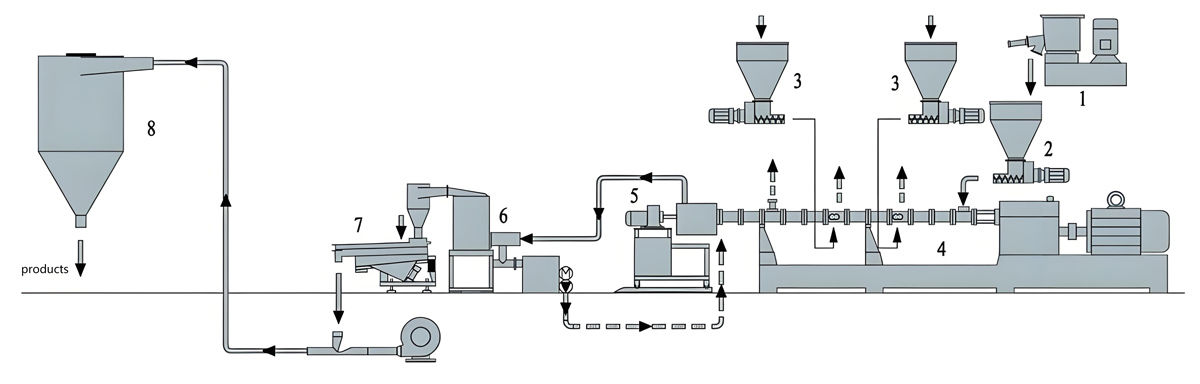
1. Basic production process flow
Raw material preparation: Accurately weigh the raw materials such as polybutylene succinate (PBS) resin, additives, fillers, etc. according to the formula ratio.
Mixing: Mix the raw materials thoroughly in a high-speed mixer to ensure even distribution of each component.
Extrusion: The mixed raw materials are added to a twin-screw extruder, and through the shearing and mixing action of the screw, the raw materials are melted and plasticized. During the extrusion process, precise control of parameters such as temperature and screw speed is required to ensure the quality and performance of the masterbatch.
Granulation: The extruded melt is cut into uniform granular masterbatch through a granulation system.
Drying and packaging: Dry the mother granules after cutting to remove moisture, and then package them for storage and transportation.
2. Production process characteristics of different types of PBS masterbatch
Flame retardant PBS masterbatch
Flame retardant addition: During the mixing stage, the flame retardant is mixed with PBS resin and other raw materials in a high-speed mixer.
Temperature control: Due to the potential temperature sensitivity of flame retardants, more precise temperature control is required during the extrusion process to avoid decomposition or failure of flame retardants.
Antibacterial PBS masterbatch
Antibacterial agent dispersion: Antibacterial agents usually need to be dispersed at the nanoscale in PBS resin to ensure their antibacterial effect. Therefore, special dispersion techniques such as ultrasonic dispersion and mechanical stirring are required during the mixing stage.
Avoiding pollution: Strict control of environmental hygiene is required during the production process to prevent contamination of antibacterial agents, which may affect their antibacterial performance.
Toughened PBS masterbatch
Toughening agent selection: Choose the appropriate toughening agent based on the desired toughening effect, such as elastomers, plasticizers, etc.
Processing parameter adjustment: The addition of toughening agents may affect the processing performance of PBS, such as fluidity, melt strength, etc. Therefore, it is necessary to adjust the processing parameters during the extrusion process to ensure the quality and performance of the masterbatch.
Fill PBS masterbatch
Filler selection: Choose suitable fillers according to application requirements, such as calcium carbonate, talcum powder, glass fiber, etc.
Dispersion and lubrication: The degree of dispersion of fillers in PBS resin has a significant impact on the performance of masterbatch. Therefore, effective dispersion techniques need to be adopted during the mixing stage, and lubricants should be added as necessary to improve the dispersibility and processing performance of the fillers.
3. Precautions
Accurate formula ratio: The formula ratio of different types of PBS masterbatch varies, and it is necessary to accurately weigh each raw material to ensure the accuracy of the formula.
Strict temperature control: Temperature control during the extrusion process is crucial for the quality and performance of the masterbatch. It is necessary to accurately control the temperature of each heating section based on the characteristics of the raw materials and processing requirements.
Reasonable screw design: The design of the screw has a significant impact on the mixing and plasticizing effect of the masterbatch. It is necessary to select the appropriate screw structure and parameters based on the characteristics of the raw materials and processing requirements.
Environmental hygiene control: Strict control of environmental hygiene is required during the production process to avoid contamination of raw materials, which may affect the quality and performance of masterbatch.
Production equipment
The production equipment for PBS masterbatch mainly includes extruders, feeders, dryers, vibrating screens, and conveyors, among which extruders are the key equipment.
Extruder:
Type: Double screw extruders are commonly used due to their excellent mixing and plasticizing capabilities, making them suitable for producing PBS masterbatch.
Screw design: The screw should be designed based on the principle of building blocks, in order to reasonably configure the aspect ratio, pitch, screw components, etc. according to the processing material system and process requirements. The screw material should be selected from high-quality materials that are wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant, such as 38CrMoAlA, to ensure the stability and reliability of the screw during long-term use.
Temperature control: The extruder should be equipped with a precise temperature control system that can accurately control the temperature of the barrel and head. For PBS resin, the barrel temperature is usually adjusted based on its melting temperature, typically between 110 ℃ and 120 ℃.
Exhaust system: Due to the possibility of gas generation during the plasticization process of PBS resin, the extruder should be equipped with an effective exhaust system to eliminate gas, avoid the generation of bubbles, and ensure the quality of the masterbatch.
Granulation system: The granulation system of the extruder should be able to produce uniform granular masterbatch, with adjustable granulation speed to meet different production needs.
Feeding machine:
Used to evenly feed raw materials into the extruder, ensuring the continuity and stability of the extrusion process.
Drying machine:
For PBS resin with strong moisture absorption, it may be necessary to dry it before mixing to reduce moisture content and improve the quality of the masterbatch.
Vibration sieve:
Used for screening and removing unqualified masterbatch to ensure uniform particle size distribution in the final product.
Conveyor belt:
Used to transport the diced masterbatch to the next process, such as packaging or storage.
These production equipment work together to complete the production process of PBS masterbatch. In actual production, it is necessary to adjust and optimize the equipment appropriately according to the specific formula ratio and production process requirements to ensure that the quality and performance of the masterbatch meet the application requirements.
PBS masterbatch extruder
Kerke’s masterbatch extruder can be used to produce PBS masterbatch. Our PBS masterbatch extruder has multiple models to choose from, which can meet different production requirements.
-

Laboratory Twin Screw Extruder
When will you need a lab twin screw extruder? If you want to make trials and tests of…
-
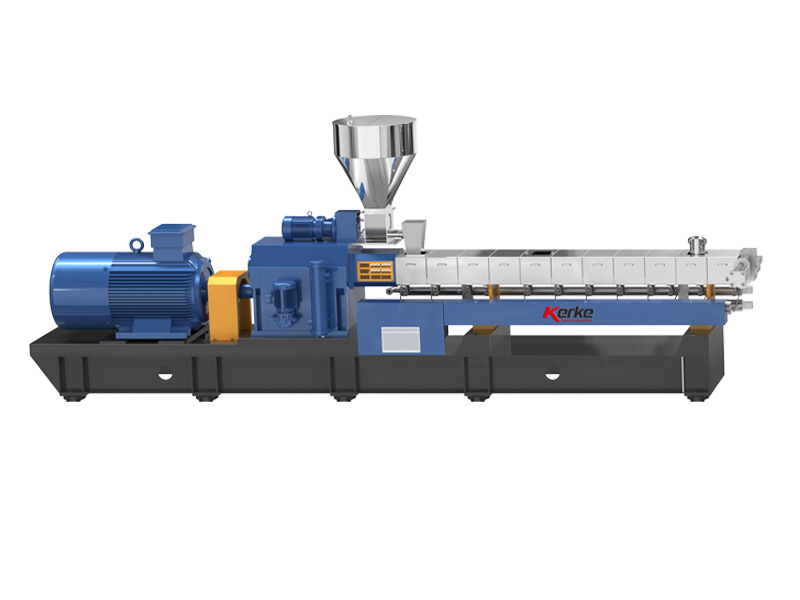
Parallel Twin Screw Extruder
Our Parallel Co-rotating twin screw extruder is designed for compounding and masterbatch making with an output capacity from…
-
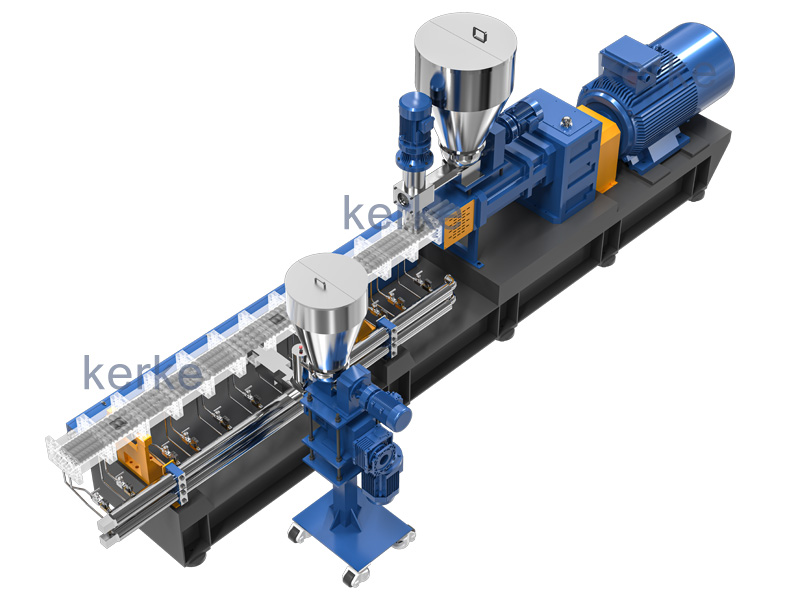
Triple (3 screws) Extruder
3 Screws extruder is a new technology that has many advantages. The triple screw extruder is mainly used…
-
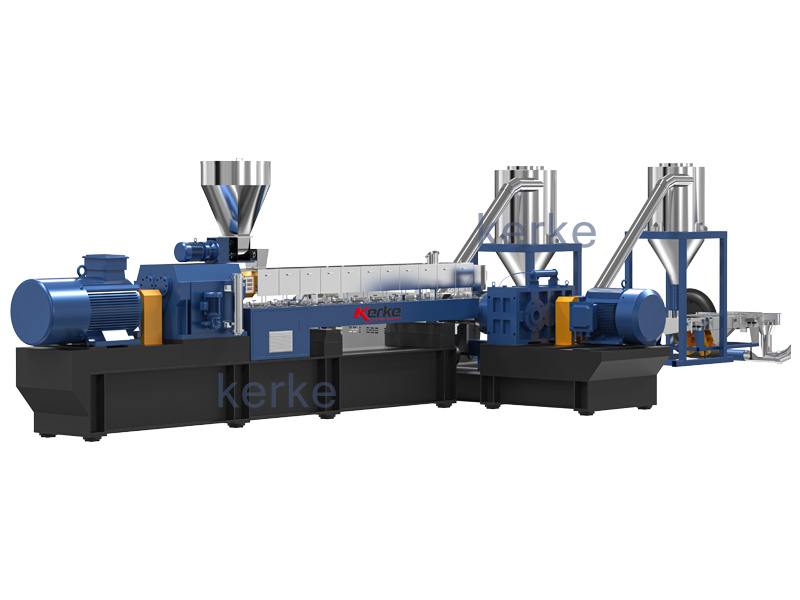

Double-Stage Extrusion System
Mother-baby extrusion system is designed for special materials which can not process on one stage extruder, the first…
-
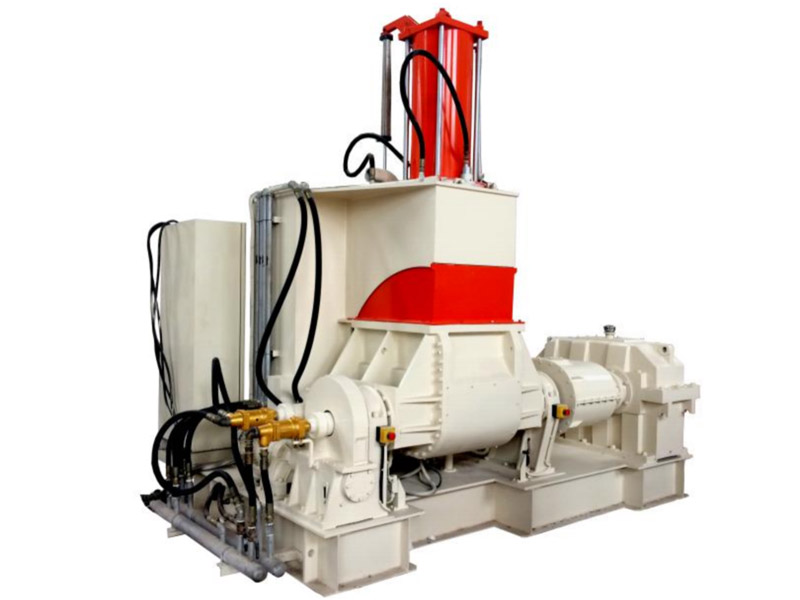

Banbury Kneader Compounding Line
Our kneader + extruder is designed for making special applications with an output capacity from 30kg/h to 1000kg/h.…
-
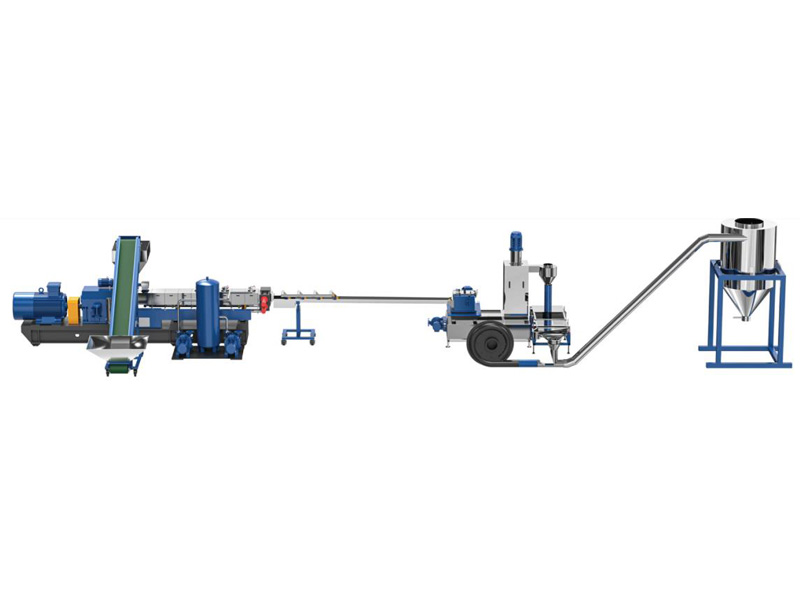
Cutting System / Pelletizing System
Different material needs different cutting system, Kerke provides all kinds of cutting system, here is the explanation of…
Related requirements
The specific requirements for the extruder used in the production of PBS masterbatch are as follows:
Temperature control capability:
Accurate temperature control: The extruder should be equipped with a high-precision temperature control system that can accurately control the temperature of the barrel and head. For PBS resin, the barrel temperature usually needs to be adjusted according to its melting temperature, usually between 110 ℃ and 120 ℃.
Segmented heating: The material barrel should be divided into multiple heating sections for segmented heating according to the plasticization requirements of the material, ensuring uniform and stable temperature during the extrusion process.
Temperature regulation range: The temperature regulation range of the extruder should be wide enough to meet the needs of different formulations and production processes.
Screw design and material:
Screw structure: The screw should be designed based on the principle of building blocks, in order to reasonably configure the aspect ratio, pitch, screw components, etc. according to the processing material system and process requirements. The shear and mixing ability of the screw is crucial for the plasticization and uniformity of PBS masterbatch.
Screw material: High quality materials that are wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant, such as 38CrMoAlA, should be selected to ensure the stability and reliability of the screw during long-term use.
Screw optimization: Based on specific production requirements, optimize the design of screws, such as using special thread structures or exhaust grooves, to improve plasticizing effect and exhaust performance.
Exhaust system:
Effective exhaust: Due to the possibility of gas generation during the plasticization process of PBS resin, the extruder should be equipped with an effective exhaust system to eliminate gas, avoid the generation of bubbles, and ensure the quality of the masterbatch.
Exhaust port design: The exhaust port should be located above the material conveying direction, with a moderate size to prevent materials from entering the exhaust system. At the same time, protective devices such as metal filters or baffles should be installed at the exhaust outlet to prevent materials from blocking the exhaust passage.
Granulation system:
Uniform granulation: The granulation system of the extruder should be able to produce uniform granular masterbatch, and the particle size distribution should meet the requirements for subsequent processing and use.
Adjustable cutting speed: The cutting speed of the cutting system should be adjustable to meet different production needs and ensure the yield and quality of the masterbatch.
Equipment stability and reliability:
High stability: The extruder should have good stability to ensure the continuity and stability of the production process, reduce failures and downtime.
High reliability: The components of the extruder should be made of high-quality materials to ensure the reliability and durability of the equipment. At the same time, regular maintenance and upkeep of the equipment should be carried out to extend its service life.
Adaptability and flexibility:
Formula adaptability: The extruder should be able to adapt to the production needs of different formulas, including the addition of flame retardants, antibacterial agents, toughening agents and other additives.
Production flexibility: The extruder should have a certain degree of production flexibility and be able to quickly adjust production plans and product specifications according to market demand.
Application
The application fields of PBS masterbatch are wide, mainly including the following aspects:
Packaging field:
Disposable plastic products: PBS masterbatch can be used to produce disposable knives, forks, lunch boxes, water bottles, etc. These products can be decomposed by microorganisms after use, reducing environmental pollution.
Packaging film: used to manufacture biodegradable packaging materials such as food bags, garbage bags, cosmetic bottles, etc., replacing traditional non biodegradable plastics and reducing plastic pollution.
In the field of agriculture:
Agricultural film: The agricultural film produced from PBS masterbatch is biodegradable and can decompose in the soil after use, avoiding pollution to the soil and crops.
Fertilizer slow-release material: By controlling the degradation rate of PBS masterbatch, it can be applied to fertilizer slow-release materials to improve the utilization efficiency of fertilizers.
Biomedical field:
Disposable medical supplies such as syringes, infusion tubes, etc. The biocompatibility and degradability of PBS masterbatch make it an ideal material for medical supplies.
Biomedical polymer materials: used to manufacture artificial cartilage, sutures, scaffolds, etc., meeting the high requirements for material biocompatibility and degradability in the medical field.
Other fields:
Golf course nails: The nails produced from PBS masterbatch are biodegradable and will not cause long-term pollution to the environment.
Seedling fixing materials for afforestation in tropical rainforests: Utilizing the degradability of PBS masterbatch to produce seedling fixing materials and promote ecological restoration.
Electronic packaging bags, plastic films, and foam materials: PBS masterbatch can also be used to manufacture these environmentally friendly products, meeting the market’s demand for biodegradable materials.
Summary:
PBS masterbatch has been widely used in various fields such as packaging, agriculture, and biomedicine due to its excellent biodegradability, good mechanical properties, and processability. With the increasing awareness of environmental protection and the growing demand for sustainable development, the application prospects of PBS masterbatch will be even broader.